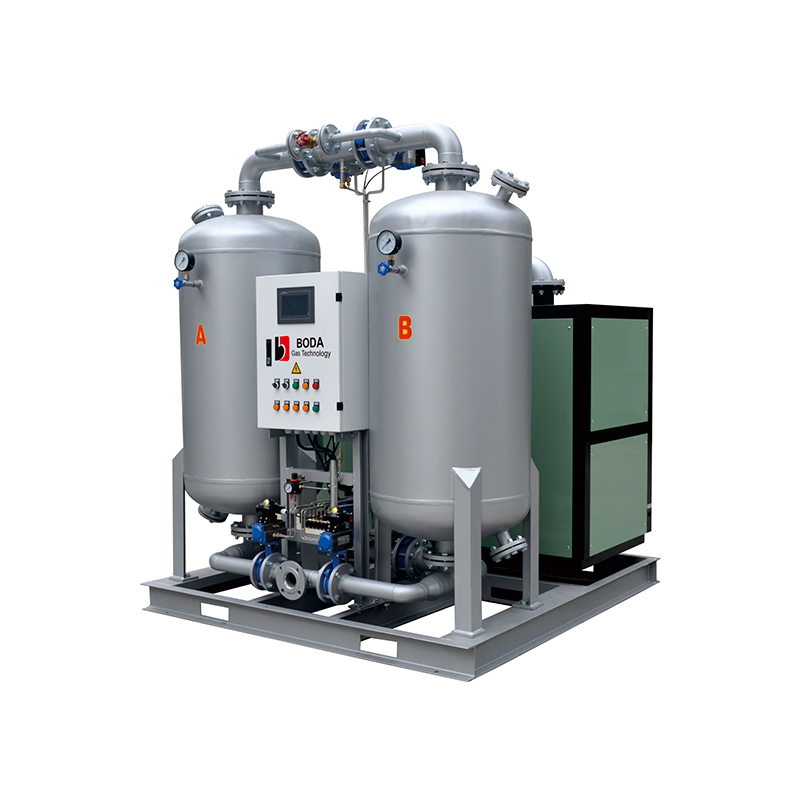
The lifespan of a nitrogen generator typically ranges from 8 to 10 years, depending on maintenance and operational conditions. Pressure Swing Adsorption (PSA) nitrogen generators rely on molecular sieves, which degrade over time, affecting efficiency. Regular inspections and timely sieve replacements help prolong their lifespan. Membrane nitrogen generators have a slightly shorter lifespan due to gradual membrane fiber wear. Maintaining clean air intake and following strict maintenance schedules are essential for extending the generator’s operational life.
Factors that affect the life expectancy of a nitrogen generator:
According to manufacturers, the typical design life expectancy of a nitrogen generator (e.g., PSA) ranges from 8 to 10 years. However, the actual lifespan varies significantly depending on usage conditions, maintenance practices, and environmental factors. For example:
- Poor air quality (oil, moisture, dust) can degrade adsorbents like carbon molecular sieves (CMS), shortening lifespan.
- Frequent pressure or temperature fluctuations accelerate mechanical wear.
- Neglecting filter replacements or valve maintenance leads to system inefficiency and premature failure.
The Five Key Factors Affecting the Lifespan of a Nitrogen Generator
Whether molecular sieves are sourced from Japan’s Takeda or domestic Chinese manufacturers, their performance declines over time. Five key factors influence the lifespan of a nitrogen generator: air quality, operating pressure, temperature control, maintenance, and usage environment. To maximize longevity, these factors must be optimized in real-world applications.
Agitate: Why do some nitrogen generators fail earlier than others? Key reasons for reduced lifespan include:
Core component degradation: Adsorbents (e.g., CMS) are sensitive to contaminants like oil or water. Even trace amounts from compressed air can irreversibly damage them.
Operational stress:
- Frequent start-stop cycles or unstable pressure/temperature conditions increase mechanical strain.
- Overloading (e.g., exceeding rated nitrogen flow/purity) accelerates wear on valves and seals.
- Environmental factors: Exposure to high humidity, dust, or corrosive gases accelerates corrosion and component aging.
- Inadequate maintenance: Skipping filter replacements, ignoring leaks, or delaying repairs can lead to cascading failures.
How to maximize nitrogen generator lifespan?
To achieve the full 8–10-year design life (or beyond), implement these best practices:
| Optimize Air Quality | Stabilize Operating Conditions | Rigorous Maintenance | Operational Discipline | Environmental Control |
| Use multi-stage filtration (coalescing filters, activated carbon) to remove oil, moisture, and particles. | Maintain consistent pressure (e.g., 0.6–0.8 MPa for PSA systems) to avoid adsorbent stress. | Replace filters (pre-filters, coalescing filters) on schedule. | Avoid abrupt startups/shutdowns; follow preheating and cooldown protocols to minimize thermal stress. | Install the generator in a clean, dry, and well-ventilated area to prevent corrosion and overheating |
| Regularly drain air compressors and check dryer performance to prevent moisture ingress. | Control ambient temperature (avoid extremes) and ensure proper ventilation. | Inspect valves and seals monthly for leaks or wear. | Train operators to adhere to standardized procedures (e.g., daily parameter checks). | |
| Monitor CMS performance: Replace carbon molecular sieves if nitrogen purity declines. |
Do nitrogen generators need compressed air?
Yes, nitrogen generators require compressed air as their raw material. The compressed air passes through filtration and separation processes, such as PSA or membrane technology, to extract nitrogen. The quality of the compressed air significantly impacts the generator’s efficiency. Contaminants such as oil, moisture, and particulates can degrade key components, leading to frequent repairs. To maintain optimal performance, industries use air dryers, high-efficiency filters, and oil-water separators to ensure a clean, dry air supply.
How to prolong the life of a nitrogen generator?
Ensure Your Compressed Air Supply is Clean and Dry
Contaminants such as oil, moisture, and dust can accelerate the degradation of a nitrogen generator. Using high-efficiency air dryers and multi-stage filtration systems removes impurities, protecting molecular sieves and membranes from damage.
Strictly Adhere to Recommended Maintenance Schedules
Routine maintenance is crucial for long-term performance. Regularly changing filters, inspecting valve conditions, and monitoring nitrogen purity help prevent unexpected breakdowns and costly repairs.
Inspect the Gauges and Indicators
Monitoring pressure levels, flow rates, and nitrogen purity is essential for detecting potential issues early. Any sudden deviations in readings indicate the need for troubleshooting and adjustments.
Utilize Onsite Nitrogen Generator Maintenance Services
Partnering with professional service providers ensures thorough inspections, efficiency tests, and timely component replacements. Expert maintenance services help prevent major failures and extend equipment lifespan.
Choose a Reliable and Customized Nitrogen Generation System
Selecting a nitrogen generator tailored to your specific application ensures optimal efficiency. Features such as energy-saving controls, remote monitoring, and customized filtration systems contribute to extended operational life.
PSA Nitrogen Generator Pros and Cons
PSA nitrogen generators are highly efficient and cost-effective, providing high-purity nitrogen for industrial applications. However, they require periodic maintenance, including molecular sieve replacement. The advantages include consistent nitrogen production and adjustable purity levels, while the main drawback is ongoing maintenance costs.
Conclusion
Optimizing air quality, adhering to maintenance schedules, and monitoring system indicators are essential for extending the lifespan of a nitrogen generator.




